
Freedom Apex Enterprise & Financial Services
"Speed Breeds Success"
"Where Building Is Helping You Win"

Click Here Now To Get More Information and Complete Survey
Click Here for Your Free Freedom Financial Assessment Plan
Benefits of Investing in Securities

Investing in securities, such as stocks and bonds, can offer a range of benefits for investors. Here are some key advantages of investing in securities:
Potential for Capital Appreciation: Securities, particularly stocks, have the potential to increase in value over time. This capital appreciation can result in significant returns on investment.
Dividend Income: Many stocks pay dividends, providing investors with a regular income stream. Dividend income can be an attractive feature, especially for income-focused investors.
Diversification: Investing in a variety of securities allows for diversification, spreading risk across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. Diversification can help mitigate the impact of poor-performing investments.
Liquidity: Securities are often traded on organized exchanges, providing investors with liquidity. This means they can buy or sell securities relatively easily, facilitating quick access to funds.
Ownership Stake: When you invest in stocks, you become a partial owner of the company. This ownership may come with voting rights and the ability to benefit from the company's success through capital gains and dividends.
Fixed Income Investments: Bonds and other fixed-income securities provide predictable interest payments and return of principal at maturity. They can be a more conservative investment option, offering stability and income.
Potential for Passive Income: Certain securities, such as dividend-paying stocks or real estate investment trusts (REITs), can generate passive income, allowing investors to earn money without actively managing the investment.
Hedging Against Inflation: Some securities, particularly assets like real estate and certain commodities, may act as a hedge against inflation. As prices rise, the value of these assets may increase.

Professional Management: Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) pool money from multiple investors and are managed by professional fund managers. This allows investors to benefit from the expertise of experienced professionals.
Accessibility: Investing in securities is accessible to a wide range of investors. Online trading platforms and investment accounts make it easy for individuals to buy and sell securities.
Information Availability: Information about publicly traded securities is readily available. Investors can access financial statements, earnings reports, and other relevant data to make informed investment decisions.
Long-Term Wealth Building: Historically, the stock market has demonstrated the potential for long-term wealth accumulation. By staying invested over an extended period, investors may benefit from compounding returns.
Retirement Planning: Securities can be an integral part of retirement planning. By investing in a diversified portfolio, individuals can build wealth for retirement and potentially generate income during their retirement years.
Tax Advantages: Some investments, such as certain types of bonds or retirement accounts, offer tax advantages. For example, interest income from municipal bonds may be tax-free, and contributions to retirement accounts can be tax-deductible.
While investing in securities can offer numerous benefits, it's essential for investors to conduct thorough research, consider their risk tolerance, and align their investments with their financial goals. Diversification and a long-term perspective are often key principles for successful investing. Additionally, seeking advice from financial professionals can help individuals make informed investment decisions.

Click Here for Your Free Freedom Financial Assessment Plan
Different Types of Securities
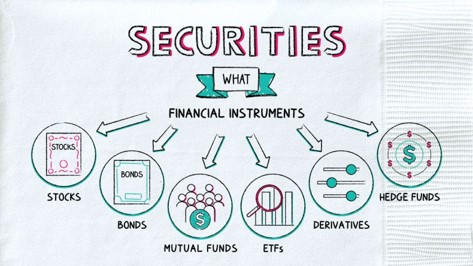
Securities are financial instruments that represent ownership in a company or a promise to repay borrowed funds. There are several types of securities, each serving different purposes and offering distinct features. Here are some common types of securities:
Stocks (Equity Securities): Common Stock: Represents ownership in a company and may come with voting rights at shareholder meetings. Common stockholders have the potential for capital appreciation and may receive dividends. Preferred Stock: Typically, does not carry voting rights but has a higher claim on assets and earnings than common stock. Preferred stockholders receive fixed dividends.
Bonds (Debt Securities): Corporate Bonds: Issued by corporations to raise capital. Bondholders receive periodic interest payments and the return of principal at maturity. Government Bonds: Issued by governments to fund public projects. Examples include U.S. Treasury bonds. They are considered low-risk and often provide fixed interest payments. Municipal Bonds: Issued by state or local governments to finance public projects. Interest income from municipal bonds is often tax-free at the federal level.
Mutual Funds: Pools money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. Managed by professional fund managers.
Exchange-Traded Funds (EFTs): Similar to mutual funds but traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks. ETFs often track a specific index or sector.
Derivatives: Financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset. Examples include options and futures contracts.
Options: Contracts that give the holder the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price before or at the expiration date.
Futures Contracts: Agreements to buy or sell an asset at a future date for a predetermined price. Futures are often used for commodities like oil or agricultural products.

Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Companies that own, operate, or finance income-generating real estate. REITs offer a way for individuals to invest in real estate without directly owning physical properties.
Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Time deposits offered by banks with a fixed term and fixed interest rate. CDs are considered low-risk but offer lower returns compared to some other investments.
Treasury Securities: Issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. Examples include Treasury bills (T-bills), Treasury notes (T-notes), and Treasury bonds (T-bonds). Considered low-risk and often used as a benchmark for other interest rates.
Commercial Paper: Short-term debt issued by corporations to fund short-term liabilities. Commercial paper is typically unsecured and has maturities ranging from a few days to several months.
Convertible Securities: Securities, often bonds or preferred stock, that can be converted into common stock at a predetermined price. This allows investors to participate in potential stock appreciation.
These are just a few examples of the many types of securities available in the financial markets. Each type of security comes with its own risk and return characteristics, and investors often build diversified portfolios to manage risk and achieve their financial goals.

Click Here for Your Free Freedom Financial Assessment Plan
Broker Check